Vinyl Siding
Vinyl Siding
Vinyl siding is most commonly seen as interlocking horizontal strips. It is also seen as vertical panels, and as strips that simulate wood shingles and shakes. It comes in many colors and finishes. It should be installed by fastening the siding to sheathed walls covered by a water-resistive barrier. This siding was first widely available in the 1960s and has been increasingly popular since then. It is currently one of the most widely installed wall coverings. This material is sometimes called polymer or polymeric siding.
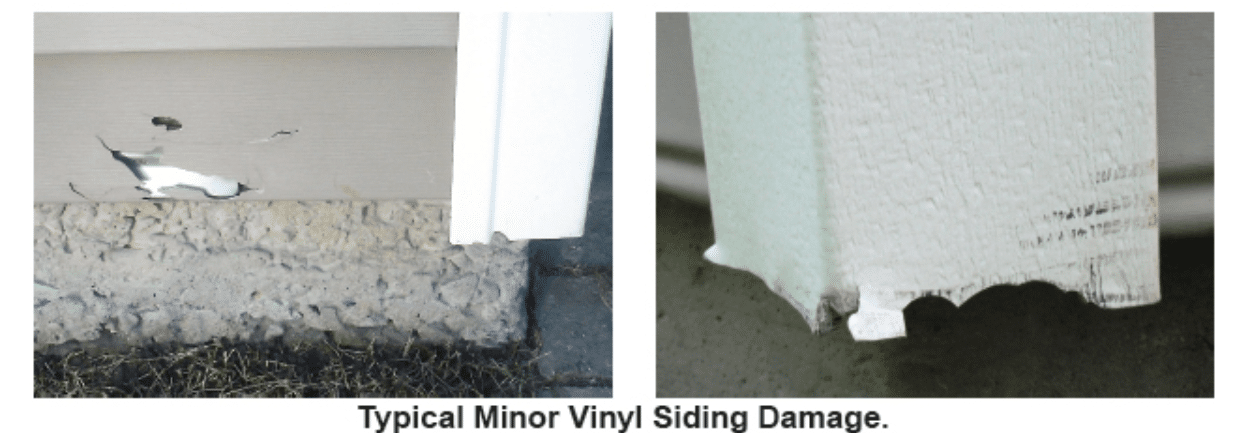
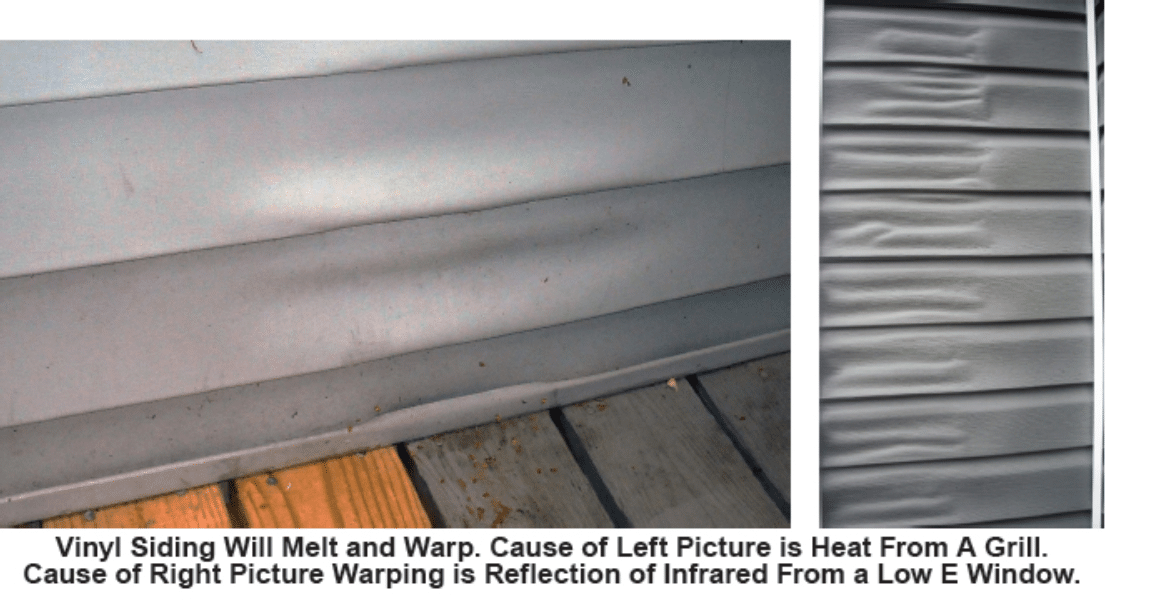
Vinyl siding is relatively inexpensive and is virtually maintenance-free. It does, however, have some disadvantages. The color can fade over time, especially on sides of the house exposed to sunlight. Vinyl siding can be painted with paint made for this purpose, but once painted it must be repainted regularly. Vinyl siding is easily damaged. It can be a challenge to replace damaged pieces with matching material. Vinyl siding is known to warp when exposed to heat, and it can become brittle when exposed to extreme cold.
Vinyl siding should be installed according to manufacturer’s instructions. These instructions may vary based on the manufacturer, the type of siding being installed, and the location of the house.
Typical Defects Typical defects that home inspectors should report include:
- absent flashing and channel trim around doors, windows, and other penetrations,
- inadequate clearance above grade, hard surfaces, and roof coverings,
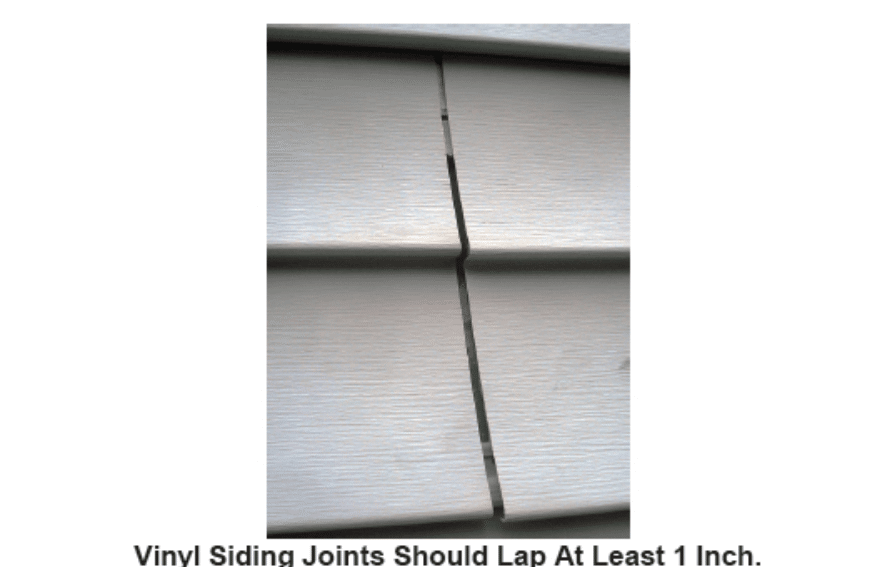
- inadequate lap at joints (about 1 inch),
- inadequate space (about ¼ inch) at vertical trim to allow for expansion,
- fastened too tight against wall; each piece should be free to move with expansion and contraction,
- absent and improperly installed flashing and kick out flashing at wall intersections,
- damage, deterioration, faded color,
- absent starter course.
Standards (1) IRC 2018 Section R703; (2) manufacturer’s instructions (must be followed precisely).